Beat Forks, 3B60.10
Topic and Concept:
Wave Motion, 3B60. Beats
Location:
Cabinet: Waves and Sound(WS)
Bay: (A1 Right)
Shelf: #1
Abstract:
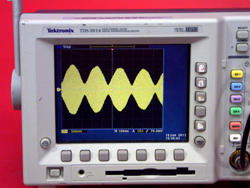
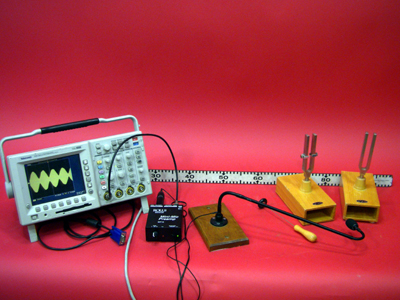
Two tuning forks differing in frequency by about 1 Hz are mounted on resonance boxes and set to vibrate together creating beats. A microphone and oscilloscope can be used to display the resultant waveform.
Equipment |
Location |
ID Number |
|
|
|
Two Tuning Forks with Resonance Boxes and Mallet |
|
|
|
||
Microphone with Preamp and 1/4" to BNC Cable |
|
Important Setup Notes:
- N/A
Setup and Procedure:
- Place two tuning forks close in frequency mounted on resonance boxes next to each other on a tabletop.
Plug in the Oscilloscope and the preamp.
- Connect the mic wire to the preamp input.
Connect the "unbal" output (1/4" jack) to the Oscilloscope channel 1 input using the 1/4" to BNC cable.
Power up the Oscilloscope and scale appropriately.
- Strike each tuning fork with the mallet, and observe the waveform on the screen.
Cautions, Warnings, or Safety Concerns:
- N/A
Discussion:
Sound waves obey the principle of superposition. When two sound (pressure) waves encounter one another, they interfere. Spatially, the resultant wave has alternating spots of constructive and destructive interference. The frequency at which these occur in time at each location is called the beat frequency. The frequency depends on the respective frequencies of the interfering waves as follows
fbeat = |f1 - f2|
|
|
|
Videos:
References: