|
Size: 2895
Comment:
|
← Revision 7 as of 2013-07-12 18:17:57 ⇥
Size: 2973
Comment: converted to 1.6 markup
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
| ||<:30%>[:PiraScheme#Mechanics: Table of Mechanics Demonstration]||<:30%>[:MEEquipmentList: List of Mechanics Equipment & Supplies]||<:30%>[:Demonstrations:Lecture Demonstrations]|| | ||<:30%>[[PiraScheme#Mechanics| Table of Mechanics Demonstration]]||<:30%>[[MEEquipmentList| List of Mechanics Equipment & Supplies]]||<:30%>[[Demonstrations|Lecture Demonstrations]]|| |
| Line 7: | Line 7: |
| Rotational Dynamics, [:RotationalDynamics#Gyros: 1Q50. Gyroscopic Motion] | Rotational Dynamics, [[RotationalDynamics#Gyros| 1Q50. Gyroscopic Motion]] |
| Line 10: | Line 10: |
| * '''Cabinet:''' [:MechanicsCabinet:Mechanic (ME)] * '''Bay:''' [:MechanicsCabinetBayA12:(A12)] |
* '''Cabinet:''' [[MechanicsCabinet|Mechanic (ME)]] * '''Bay:''' [[MechanicsCabinetBayA12|(A12)]] |
| Line 14: | Line 14: |
| attachment:ToyGyro06-400.jpg | {{attachment:ToyGyro06-400.jpg}} |
| Line 22: | Line 22: |
| ||Gyroscope||[:MechanicsCabinetBayA12: ME, Bay A12, Shelf #1]|| || | ||Gyroscope||[[MechanicsCabinetBayA12| ME, Bay A12, Shelf #1]]|| || |
| Line 47: | Line 47: |
| ||attachment:ToyGyro02-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro03-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro04-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro05-250.jpg|| ||attachment:ToyGyro06-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro07-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro08-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro09-250.jpg|| ||attachment:ToyGyro10-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro11-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro12-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro13-250.jpg|| ||attachment:ToyGyro14-250.jpg||attachment:ToyGyro15-250.jpg|| |
||{{attachment:ToyGyro02-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro03-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro04-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro05-250.jpg}}|| ||{{attachment:ToyGyro06-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro07-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro08-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro09-250.jpg}}|| ||{{attachment:ToyGyro10-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro11-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro12-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro13-250.jpg}}|| ||{{attachment:ToyGyro14-250.jpg}}||{{attachment:ToyGyro15-250.jpg}}|| |
| Line 53: | Line 53: |
| * [https://www.youtube.com/user/LectureDemostrations/videos?view=1 Lecture Demonstration's Youtube Channel] | * [[https://www.youtube.com/user/LectureDemostrations/videos?view=1|Lecture Demonstration's Youtube Channel]] |
| Line 57: | Line 57: |
| * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gyroscope Wikipedia - Gyroscope] * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_momentum Wikipedia - Angular Momentum] * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nutation Wikipedia - Nutation] * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Precession Wikipedia - Precession] |
* [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gyroscope|Wikipedia - Gyroscope]] * [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_momentum|Wikipedia - Angular Momentum]] * [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nutation|Wikipedia - Nutation]] * [[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Precession|Wikipedia - Precession]] |
| Line 64: | Line 64: |
| [:Instructional:Home] | [[Instructional|Home]] |
Precessing Toy Gyroscope, 1Q50.51
Topic and Concept:
Rotational Dynamics, 1Q50. Gyroscopic Motion
Location:
Cabinet: Mechanic (ME)
Bay: (A12)
Shelf: #1
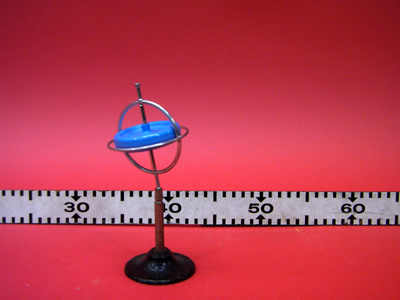
Abstract:
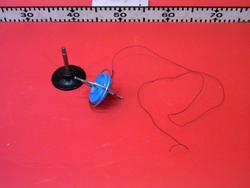
A pull string gyroscope precesses around an axis.
Equipment |
Location |
ID Number |
|
|
|
Gyroscope |
|
Important Setup Notes:
- This demo may require practice.
Setup and Procedure:
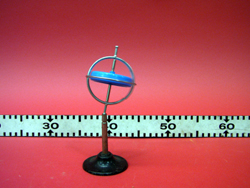
- Place the stand on a table.
- Locate a small hole on the axle of the gyroscope. Take one end of the black string, and feed it through the hole about an inch.
- Neatly wind up the string around the axle.
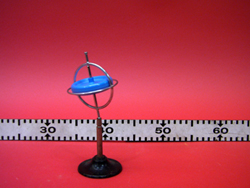
- Now place the gyroscope on the stand so that the axle is vertical. Press down with a finger on the top "ball" to keep the gyroscope in place.
- With your free hand, grab the string and give it a continuous pull until the string is completely out.
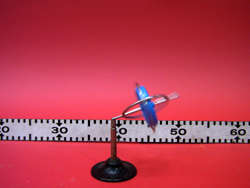
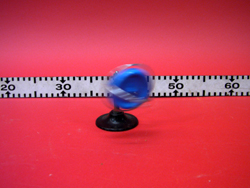
- You can now release the gyroscope. It will begin to precess due to the torque of gravity.
Cautions, Warnings, or Safety Concerns:
- N/A
Discussion:
Once the wheel is spinning, it has angular momentum. The amount can be increased by making the wheel spin faster. Since angular momentum is conserved, the rotational axis of the wheel will remain in place. This would be the case if there were not any torques acting on the wheel. In our case, this net torque is due to the gravity. The resultant effect is that our wheel precesses around the original axis.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Videos:
References: